PART 8. The MYSOREAN NAVY
The Mysorean navy is very much a creature of mystery. We know that the state had a navy -and quite a powerful one too for the region, but finding information on it is fraught with problems, not least of which are the numerous regurgitations of spurious information across the internet and within history books, particularly those looking at Tipu Sultan “in a new light” re-casting him as a freedom fighter and patriot rather than as a tyrant and religious zealot.
In “The Navy In India 1763—1783” Admiral Sir H Richmond gives us the following description of the cutting out expedition against the Mysorean Navy in Mangalore harbour in 1780:-
 |
| Illustration 102: Grabs and Galivats attacking East Indiamen |
In 1775, the future admiral Nelson, then a mere Midshipman under Cpt. George Farmer aboard the 24 gun frigate “Seahorse” in convoy with the East Indiaman “Dodley”. In the mistaken belief that they were Mahratta vessels, with whom Britain was at war, Farmer engaged two of Haidar Ali’s armed cruisers.
“At 7 [a.m.] saw two sail standing toward us, which we imagined to be
Bombay cruisers, at ½ past 7 they hauled their wind to the southward
and stood after the Dodley, and hoisted Haidar Ali’s colours, we immediately tacked and stood after them, at 8 fired several shot to bring one of them too.”
It’s quite telling that Farmer took these vessels to be ships of the Bombay Marine -the EICs own navy, indicating the similarity in appearance to European ships and sail plans.
According to the French historian, Joseph Michaud (1767–1839), Haidar Ali was clearly building his navy with military intent. Michaud confirms the dockyard at Mangalore as Haidar Ali’s premier yard, and:
“a navy had begun to be built there, intended to free the Indian ocean one day from the European pirates.”
Referring to the British capture of Mangalore in 1780, he confirms:
“Three ships of the line with fifty or sixty cannon had been completed; many others of varying sizes were in process of construction; and the English found considerable materials to equip a fleet with.”
Despite this setback, by 1782 we know of at least the following ships in Tipu's navy from a table in the above book. This list shows the most common types of ships used by the Mysorean navy. The 60 gun ships would have been small men of war and the 36 and 20 gun ships frigates.
The British saw the Navy of Mysore as a grave threat to their maritime dominance as its’ size gave it a greater force than the Royal Navy and Bombay Marine could combine locally and, where threatened by greater force, the Mysorean ships would disappear into shoal waters or one of the numerous rivers where the deeper draughted European vessels could not folllow.
The ultimate downfall of the Mysorean navy wasn’t so much caused by the ships themselves, or even crews, which were considered to be as good as, if not better than, those of the Royal Navy or HEIC, but by the lack of protection for the harbours in which they were based. Even after Hyder and, later Tipu had ordered defensive batteries to be built to protect the harbours and fleets, these proved to be so badly sited that they were all but useless.
The Ghurab
 |
| Illustration 104: HMS Trincomalee, a teak frigate built in Ceylon |
 |
| Illustration 105: A Ghorab |
The Galivat
A galivat or galbat was a large rowing or sailing boat 60-70 feet long, narrow in the beam and with one or two lateen sails and a spar deck made from split bamboo for lightness. Their manoeuvrability allowed them to close with better armed vessels from the bows and stern where fire was less severe, particularly in calm weather whilst their shallow draft allowed them to be run ashore safely.
Tarandes were large, three masted galivats,
 |
| Illustration 106: A Mahratta Galivat |
Note the extreme angle of the stem-post to the keel and the way the foremast is stepped where they meet.
Indian ships were generally classed in one of two groups -longships and roundships, which as the names suggest were determined by beam. Longships were narrow and fast, gathering speed quickly whilst the round-ships were broader, slower and more sea-kindly and roomy so that the names became almost synonymous with “warship” and “merchant-ship,” though round-ships were occasionally used as warships and smaller vessels were never really categorized as one or the other.
 |
| Illustration 107: The hull of a galivat |
Dangis/dingis/dingas,
- Originated in Muscat where Mysore had a factory. They had two lateen rigged masts and the stepped keel common in many Indian Ocean vessels. They made excellent “tramp” ships. “The Elements and Practice of Rigging and Seamanship” ” however gives the following description:-
“Bombay Barks, called dingas are vessels used at Bombay and places adjacent; and are navigated sometimes by rowing with paddles. They have one mast, onethird the length from the stem, which rakes much forward. On the mast is hoisted a sail, bent to a long yard, resembling a settee-sail. The tack is made fast to the head of the stem, and the sheet to the heel of the mast.
 |
Illustration 108: A dangi/dingi/dinga |
 |
Illustration 109: a dangi's hull |
These vessels never tack, but wear, in doing which they peek the yard against the mast to shift the sail; at the same time they pass the sheet before the mast. Their rigging consists of a pair of haliards, a bowline, and brace. Their keels are very much hollowed upwards, to avoid wholly grounding on sand banks.”
This “upward hollowed” keel is obvious in the hull plan and is common to many Indian Ocean vessels as well as dhows, boums, bathors, It was of course very easy to convert merchant vessels into warships when necessary.
The Snow
Snows became popular in the New World during the 1770s though rarely used by European navies. The main difference between a brig and a snow was a short “snow” or “jack” mast placed about two feet abaft the main mast which supported a large, loose footed gaff sail.
The word 'snow' comes from 'snauw' which is an old Dutch word for beak; a reference to the characteristic sharp bow of the vessel. The snow evolved from the (three-masted) ship rigged vessels: the mizzen mast gradually being moved closer towards the mainmast, until the mizzen mast was no longer a separate mast, but was instead made fast at the main mast top. As such, in the 17th century the snow used to be sometimes classified as a three-masted vessel.
The snow dates back to the late 17th century and originally had a loose footed gaff sail, the boom was introduced somewhere in the 18th century. It was a popular type of vessel in the Baltic Sea and was employed by a large number of nations during its time. The snow was considered a handy and fast sailing vessel, typically the largest two masted vessel around and was employed in both navy and merchant service. When used as a military vessel, snows were, in the early 18th century, typically fitted with 5 to 16 guns. Military snows were mostly used for coastal patrols and privateering, while in the merchant service, snows traded all the way to the Mediterranean and sometimes even sailed as far as the West Indies.
While the snow and the brig appear closely related, this is not the case. The two rigs developed from different directions, the brig evolving from the generally smaller brigantine, and the much older snow evolving from the larger Three masted “ship rigged” vessels.
The use of the characteristic snow or jack-mast offered several advantages over attaching the gaff directly to the main mast. The yoke (or jaw) of the gaff and the lacing of the gaff sail on a snow could move freely on the snow mast, not hindered by the iron bands that held together the (main) mast, nor limited by the main yard. As a result of the latter, the gaff could be raised higher than the main yard and independently of it. The resulting freedom allowed a snow, in contrast to the brigs, to fly a main course without complications, as they typically did.
However, in the late 18th century, brigs started to set main courses as well, which gave rise to the term snow-brig. Because of the size of driver or spanker sail the snow could carry and its' ability to carry a mizzen course on the jack spar (a lower sail on the spar used as a spreader for the mizzen main sail) they were considered fast ships.
 |
| Illustration 110: A Snow. Note the jack mast just behind the main mast |
 |
| Illustration 111: Two Naval Snows 1759, By Charles Brooking |
The Ketch
In modern terms, a ketch is a two masted vessel in which the fore mast is taller than the mizzen and normally fore and aft rigged. During the 18th Century this was not necessarily the case, just as a “sloop of war” could have one, two or even three masts.
Because the main mast was stepped so far back giving plenty of space on the fore deck, ketches were often used as “bombs” -ships for carrying mortars for attacking land based fortifications.
 |
| Illustration 112: An Indian Bomb Ketch of unknown nationality. It is possibly British but the same in design as those used by Hyder Ali from 1775 |
 |
| Illustration 113: A more usual ketch sail plan |
The Kotya
The Khotya, was a fast, medium sized two masted vessels used as merchantmen and war ships. It was favoured by most Indian states as well as by Europeans as "country" ships.
 |
| Illustration 114: A Kothya |
 |
| Illustration 115: The lines of a kothya. Note how far back the stem post and keel meet |
 |
| Illustration 116: A model kothya in 15mm scale |
Bugaloos
Bugaloos (baggalas) were large ocean-going dhows with poop- decks and rounded sterns.
 |
| Illustration 117: Bggala lines |
 |
| Illustration 118: A baggala/bugaloo/budgerow deep sea dhow |
 |
| Illustration 119: The ornate stern of a baggala |
 |
| Illustration 120: A Baggala at anchor |
Cutches
– Large, single masted ships with a lateen sail.
 |
Illustration 121: A cutch. |
 |
| Illustration 122: The lines of the same ship |
Phaetamars
 |
| Illustration 123 The lines of a phaetamar. The stepped keel is typical of many Indian vessels |
 |
| Illustration 124: A phaetamar. |
 |
| Illustration 125: A large modern phaetamar or pattemar under full sail |
Sambuks or sambouks
Sambuks or sambouks are medium sized dhow rigged vessels with two masts similar to those of a kothya but the mizzen sail was smaller in proportion to the mainsail
 |
| Illustration 126: Lines of a sambouk or sambuk |
 |
| Illustration 127: A Sambouk |
 |
| Illustration 128: A "modern" Sambouk |
Machavas
 |
| Illustration 129: Machava lines |
 |
| Illustration 130: A unachava/machava |
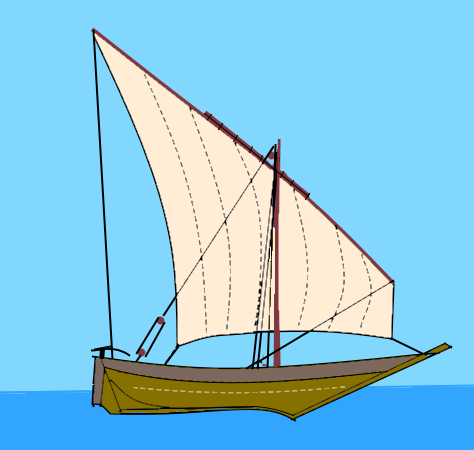 |
| Illustration 131: A mashwa:-a small inshore vessel with lateen sail |
 |
| Figure 132: A dhow. These were common throughout the Indian Ocean |
 |
| Figure 134: A dhow under sail |
her types of ship used by Indian navies were tarus, which were large ships having three to five masts, shibads/Sibadis -large, armed merchantmen that often accompanied warships carrying large numbers of troops. They were very beamy, about 150 tons burthen and had no decks. padavs -small, mainly cargo boats of 5-10 tons pagars -dug-out canoes with no outriggers, tirakatis -a three masted ship-
Boums
Boums were large craft favoured as country traders and troop carriers. They were characterised by the stern post being at the same angle as the stem post
 |
| Illustration 135: A Boum or boom |
 |
| Illustration 136: A Ghurab or Grab |
Not content with setting out his dream for the army in the Futtah al Mujahaddin, Tipu also set to work planning the restructuring and re-building of the Navy. Many on-line sources -particularly Indian sites mentioned earlier, attempting to re-brand Tipu, appear to believe he actually achieved his aims. This is purely a case of wishful thinking. Had Mysore acquired a powerful navy, it would have been cause for major naval conflict in the region and this just never happened. Apart from anything else, Tipu's plans were completely unrealistic in terms of the number of men required to man his fleet, but it does show that he understood Mysore's need for a deep-water fleet if it was ever to be master of its' own destiny. The following is taken from Kirkpatrick's translation of the Futtah al Mujahaddin. It gives a rare glimpse into Tipu Sultan's mind and his plans for the future of his domain. I feel that although it is doubtful these plans ever came to fruition it is well worth knowing of them and so I have included the regulations here for the reader to make up their own mind about.
 |
| Illustration 138: The fort and harbour at Mangalore |
 |
| Illustration 136: A Pinnace or yacht |
 |
| Illustration 137: A sloop |
I. On the Jamalabad Station:- 6 Line of battle Ships, viz. 3 of 72 guns each, and 33 of 62 guns each
 |
| Illustration 138: Mangalore |
30 Meer- Buhrs, viz. 20 Stationed to ships (being two to every Fouj, or
squadron, of four ships.) 10 at the Presence, (The Sultan) for instruction,
The land establishment of each Kuchurry was fixed as follows:-
 |
| Illustration 139: A padav |
 |
| Illustration 140: A Ghurab and a Pal |
 |
| Illustration 141: A bark or barque |
Part 11: Glossary of Indian terms.
Most of these words are concerned with the Mysorean forces, but some are Marathi. It is not a complete list as I am still adding to it.
Aftabgir:
An ornamental sun shade awarded to high officers.
Ahmadi, ahmudi:
Slave or POW infantry from the Malabar coast. Possibly Christian
ambarkhana:
A granary. Marathi
Assad-ilahi:
Slaves brought up as Moslems and trained as soldiers since childhood. The
equivalent of janissaries or Mamluks.
Askar, Uskar:
Regular cavalry with the same root as Askari
baggala/bugaloo/budgerow:
A large deep sea dhow. with poop- deck and rounded stern.
Bakhshi, bukhshi:
Originally the pay-master of a Mysore cushoon but its' commander after about
1790 . Possibly related to the term for “squeeze” or a bribe-Bakhshish
Bargirs:
Regular cavalrymen paid and equipped by the state.
bathor:
A type of merchant ship
bazar/bazaar:
The market in an army camp. Each major leader within a camp would have one
in front of his own tent and under his own banner.
Bedars:
Irregulars
Beenee Wala:
quarter-master general
Bhistie:
A water carrier
boum:
A deep sea dhow
Brinjaries, brinjaras:
Nomadic grain merchants who formed the basis of the commissariat for all Indian
armies. A kind of “white ox man.”
Bukmar:
“stinging wasp” a blunderbuss shotgun
Chauth:
A “contribution” to stop pillaging -a sort of Maratha protection money with
“chauth” signifying ¼. Marathi
compoo:
A brigade. Marathi.
Cundachars:
Tax collectors (I think. But can't find a meaning for) Mysore
Cushoon:
Originally a brigade in the Mysore army but later on a regiment.
cutch.:
A large, single masted ships with a lateen sail.
Cutcheries, Cuchurries, Kuchurries: (singular, Cutchery)
A brigade in the army of Mysore from around 1790
dangis/dingis,- Originated in Muscat where Mysore had a factory. They had two
lateen rigged masts and the stepped keel common in many Indian Ocean vessels.
They made excellent “tramp” ships.
darukhana:
A powder store. Marathi
dhows:
fast, seaworthy vessels of a range of sizes originating in the Arabian Gulf and
Red Sea.
ekas, ekandas:
silhedars volunteering for service as individuals. Marathi
Farman:
A letter of authorisation from the head of state (or rival).
Faujdar:
military governor
galivat/galbat:
was a large rowing or sailing boat 60-70 feet long
Gardi:
Often used to mean slave soldiers, but can also be used for troops trained in a
European manner (from “guards”) The term implies some sort of special quality.
Ghurab/ghorab:
A two masted warship like a corvette or small frigate with a galley-like beak at the
same level as the main-deck.
Goodurees :
Daily markets in a camp
Harcarahs, hircarahs:
scouts or guides
Havaldar:
The lowest Maratta officer rank in charge of 25 men
Hazari:
A Maratta officer over 10 Jumledars (10x 125 horsemen) or 2-3 foot
Jumledars(100-150 infantrymen)
jaghir/jageer:
A fief awarded by the ruler.
jaghirdar:
A fief holder owing allegiance to his ruler. Marathi
jaish:
Mysore infantry
Jouz weight:
The weight of eight nutmegs.
Jumledar:
An officer of 5x Havaldars (5x 25 horsemen) or 5x naiks (50 infantrymen.)
Juq, jowk:
A company. Mysore
Juqdar, jowkdar:
A company commander, a captain.
Kamaishdar:
A tax collector. Marathi
Khotyas,-
Fast, medium sized two masted vessels used as merchantmen and war ships
Khulasies:
Sailors.
machava/unachava:
A large 2 masted dhow rigged ship.
Mashwa:
a small inshore vessel with lateen sail
Mir:
Honourific for a Mysorean general or member of the staff
Mokum:
A Mysore cavalry regiment
Mukkaddam:
Governor of a town/village. Marathi.
Musnud:
throne
Mutassadi:
commander of 10,000. Mysore
Naik:
A corporal or sargeant commanding 10 infantrymen
Nalbandi:
Shoeing allowance for cavalrymen paid as part of their salary.
Nukas:
See Goodurees
unachava/machava:
A large 2 masted dhow rigged ship.
Padavs:
-small, mainly cargo boats of 5-10 tons
pagars:
dug-out canoes with no outriggers,
pals:
-three masted ghorabs. 2) tents
Palki or Nalki:
A palanquin, the use of which was awarded by the head of state to officers and
officials.
Palpatti, palputtee :
A tent tax charged on every tent in the bazar/bazaar in an army camp. Marathi
Panch Hazari:
A Marrata officer in charge of 5 Hazari (5x 1,250 men)
Peshwa:
Maratta prime minister. Eventually a hereditary position
pettah:
a civil settlement outside a fort. A suburb.
phaetamars/pattemars:
large 3 masted dhow rigged vessels, often with top, head and stay-sails
Poligar:
Leader of a small independent province or state
Rajbabthi:
A royal perquisite
Rakhi:
12.5% tax on the revenue of a district.
Raiyats:
peasants. Marathi
risala:
A battalion of infantry or a squadron of cavalry in Mysore.
risaldar:
A battalion commander, roughly equivalent to a lieutenant colonel
Sambuk/sambouk:
A medium sized 2 masted dhow rigged vessel.
saranjam:
A fief in lieu of stipulated service. Marathi.
saranjamdar:
The holder of a saranjam fief and pledged to raise an agreed number of horsemen
between 1 and 22,000 for the ruler.
Sardeshmuki:
a tax of 10% on the raiyats (peasants) Marathi
saristadar gumashta:
tax collector of Sardeshmuki. Marathi.
Sarnobat:
Chief Maratta cavalry commander responsible only to the king
saryasaqchi:
An officer who's duty was to visit his risala every day, observe its' condition and
report first to the sipahdar and then to the jaish cutchehry of the huzur (I have
been unable to find out anything concerning this officer) and finally to the Sultan
himself.
shibads/Sibadis
-large, armed merchantmen that often accompanied warships carrying large
numbers of troops. They were very beamy, about 150 tons burthen and had no
decks.
Shub-khoon:
A night assault. Mysorean
Shutarnal:
Literally “camel barrel,” also known as a Zamburak, a swivel gun mounted on a
swift camel and usually deployed en-masse.
Silhadar/silhedar:
A cavalryman responsible for providing his own horse and equipment
Sipahdar:
Commander of a Mysore regiment (or brigade before 1790)
subhas:
provinces. Marathi.
Sur (or Head) Vusdhchy:
Brigade Major.
Syce:
A groom
Talwar,Tulwar:
A curved sword or sabre.
Taramandalpet:
Galaxy or Constellation Market -the areas where rockets were constructed
tarandes:-
large, three masted galivats,
tarus,
large ships having three to five masts,
tirakati -
a three masted ship
Tope:
a wood, grove or orchard
Vaknavis:
Head of intelligence. Marathi
wakil:
An emissary. Mysore
yasaqchi:
a subaltern who's duty was to keep the senior officers in touch with the men,
report to them on the men's condition and carry their orders to their
subordinates in time of war.
Yaz or Yooz:
Mysore. A company
Yazaqdar, Yoozdar:
Commander of a yaz/yooz. Equivalent to a captain
Yusakchies:
Adjutants
Zamburak:
also known as a Shutarnal, literally “camel barrel.” a swivel gun mounted on a
swift camel and usually deployed en-masse.
Zamindar:
Governor of a city. Marathi
Part 12: Bibliography and sources.
Advices To And From India, Relative To The Cause, Progress, And Successful
Termination Or The War With The Late Tippoo Sultaun. pub 1800
A View Of The Origin And Conduct Of The War With Tippoo Sultaun
pub 1800 Alexander Beatson,
“A Narrative of the Campaign in India Which terminated the War with Tippoo
Sultan in 1792.” pub 1793. Major Dirom
“Haidar Ali And Tipu Sultan And The Struggle With The Musalman Powers Of The
South” 1893 By Lewin B. Bowring,
“Historical Sketches of The South Of India, In An Attempt To Trace The History Of
Mysoor.” Vols. 1 and 2 1817 Col. Mark Wilks
“The History Of Tipu Sultan.” Pub 1963 Mohibbul Hassan
“Select Views In Mysore.” 1794 By Mr. Home;
“War, Culture and Society, in Early Modern South East Asia 1740-1849” 2017
Kaushik Roy
“Historical Sketch Of The Native States Of India” 1875 Col GB Mallenson
“A History Of The Deccan” Vols 1-2 1924 By J. D. B. Gribble
“The Navy In India 1763—1783” pub 1936. Admiral Sir H Richmond
“Narrative Sketches of the Conquest of Mysore.” Pub 1800
“A history of the Maratha navy and merchantships.” 1973 by Dr BK Apte
“Indian Shipping. A History Of The Sea-Borne Trade And Maritime Activity Of The
Indians From The Earliest Times” 1912 by Radhakumud Mookerji, M.A.
“Rulers Of The Indian Ocean” 1927 Admiral G.A. Ballard, C.B.
“Tiger of Mysore” 1973 Denys Forrest
“The Life of Hyder Ali” 1786 Cpt. F Robson
“The History Of The Reign Of Tipu Sultan.” 1864 Col. W Miles
“A Journey From Madras Through The Countries Of Mysore, Canara, And Malabar” 1807 Francis Buchanan MD.
“History of Mysore 1399-1799 AD” Vol 3. 1943 C. Hayavadana Rao
“British Seapower and the Mysore Wars of the Eighteenth Century” by Philip
Macdougall in “The Mariner’s Mirror” Volume 97, number 4 Nov.2011
“Trade In The Eastern Seas 1793-1813.” 1937 By C. Northcote Parkinson
“Mast and Sail in Europe and Asia” 1906 H. Warington Smythe
“The Elements and Practice of Rigging and Seamanship” London 1794
“THE ARMY OF THE INDIAN M0GHULS: ITS ORGANIZATION AND ADMINISTRATION.” by WILLIAM IRVINE. London 1903







